RFID Tags
RFID tags are the most reliable elements for automatic control of subjects and objects individually. Its operation can be summarized in four steps:
- Each item has its own label, this label identifies it with a unique number that it does not share with any other item, it is the ID of each item.
- The movement of these ID numbers is automatically controlled by a radio frequency transmitter that “interrogates” the RFID tag chip.
- RFID tag ‘responds’ to the information stored in its chip by radio frequency.
- An RFID reader collects the information from the chip and stores it in a server for computerized management.
All this exchange of information between RFID tags and devices is very fast, so the updating of databases is instantaneous in real time.
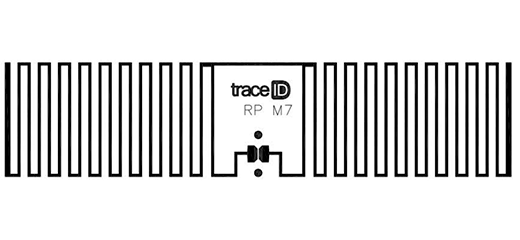
At Trace ID, we are developers and manufacturers of RFID tags, mainly UHF RFID tags but, to a lesser extent, also HF RFID tags. We also produce dual RFID tags, which are one of our new areas of development. We can supply both standard and custom RFID tags according to the customer’s needs.
The standard formats are as follows:
- First, dry inlays, are the most basic form, simply the antenna with the chip inserted.
- Secondly, wets. They are standard-sized non-customizable adhesive labels without a front, so they cannot be printed.
- Thirdly, white-wets. They are standard-sized, non-customizable adhesive labels with a front, so they are printable.
These standard formats have a set size and limited options for materials. They can be encoded, but only white-wet can be printed because they have a front. All these size and material specifications are described in the downloadable technical sheets that accompany each model in our catalog below. You will find more information on how to understand an RFID tag data sheet in this link.
Custom formats are:
A wide range of RFID tags, or smart tags, as you wish to call it. RFID tags can be tickets, stickers, hanging tags and other formats. In this type of RFID tags, customers can choose the size, materials, colors, printing data, encoding… But customization must always follow the technical conditions of manufacturing and engineering.
Know the formats we offer for any type of project.
Let's find the best solution your RFID system needs. Contact us for more information focused on your needs.
Let's talk!Know some of the sectors where our RFID tags are applied
When we talk about RFID technology, we are referring to the acronym for radio frequency identification. Therefore, the primary purpose of implementing RFID systems is item tracking. But in the case of RFID systems, this tracking is unique to each item.
Unlike barcode-based systems, RFID achieves individual identification of each item in a batch.
Generally speaking, explained in a very basic way, RFID systems consist of an RFID reader, an RFID tag, a management application, and a database.
In addition, RFID systems communicate and operate based on different standards and protocols. In summary, they operate at different frequencies and, depending on this frequency, we can divide RFID systems into three: LF, HF and UHF with different protocols for each one.
First, Low Frequency (LF RFID) covers from 125 kHz to 134 kHz and offers a read range of 10 cm.
Secondly, High Frequency (HF RFID) typically operates at 13.56MHz and has read ranges from 10cm to 1m.
Finally, Ultra High Frequency (UHF RFID) covers 433MHz and between 860MHz and 960MHz. The reading range of UHF systems can be up to 12 meters. UHF has a faster data transfer rate than LF or HF. You can find more information about this topic in our article: UHF RFID Standards and Protocols.
In particular, UHF tags are the right choice when we want a quick read of numerous elements simultaneously at a distance of no more than 12 m. Furthermore, UHF RFID tags are cheaper than LF and HF tags.
Finally, we have to specify that if UHF RFID tags are equipped with their own battery, they can reach greater distances, up to 30 meters. RFID tags without battery are called passive tags, and those with battery are called active tags.
To manufacture, we have Mühlbauer machines for inlay bonding. On these machines, chips are assembled into antennas to produce inlays. We also have converting machines from Mühlbauer, where inlays are transformed into RFID tags, wets, white-wets or appropriate RFID tags according to customer needs. As an optional last step, Trace ID has printing and coding lines. In addition, we can test our products with Voyantic RFID testing solutions in our factory.
You need an RFID system whenever you want to track individual items. The areas are very varied, but the main ones are the following:
- Supply Chain
- Logistics
- Inventory
- Retail (from clothing, shoes and accessories to jewelry)
- Access Control
- Sports Events
- Entertainment Events
- Public transportation (from urban transport tickets to airline baggage control)
- Pharmacy
- Healthcare (from hospital assets to personalized patient medication)
- Industrial Automation
- Food industry (from animal marking for traceability to retail food sales)
- And more…
The selection of the correct RFID tag depends on the specific conditions of the RFID implementation. Environment characteristics, distances or the speed of movement of the element are just some of the things to consider.
Trace ID RFID tags are customized according to customer needs with various materials and adhesives, from paper or polypropylene to foam. For example, Trace ID RFID tags are developed taking into account the difficulties that radio frequency can have to work. These can be environments with a high presence of metals or a high dielectric charge.
Contact us for more information focused on your needs.
Let's talk!The magazine of the RFID industry
The magazine to know the Benefits of RFID, to have the answers to the Frequently Asked Questions about RFID, and to stay up to date on the main news of the RFID industry.
Contact us for more information focused on your needs.